I. Introduction
This data structure is used to solve “Dynamic Connectivity” problem.
1. Applications
- Pixels in a digital photo.
- Computers in a network.
- Friends in a social network.
- Transistors in a computer chip.
- Elements in a mathematical set.
- Variable names in Fortran program.
- Metallic sites in a composite system.
2. API
61b和Algorithms两门课提供api的method名称虽然有差别,但意思是一样的。


1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// API of 61b
public interface DisjointSets {
/** connects two items P and Q */
void connect(int p, int q);
/** checks to see if two items are connected */
boolean isConnected(int p, int q);
}
3. 模型范例
4. 用户如何使用API
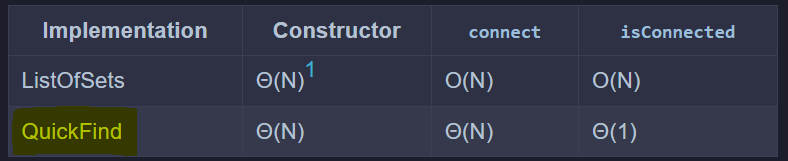
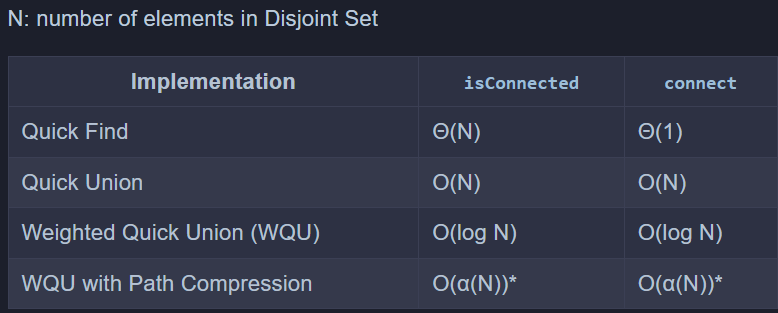
II. Quick Find
1. 原理
- 用array的indice表示N个项目。
- 用array的value表示所属的set,用来判断是否连通(value相同的indice表明互相连通)。
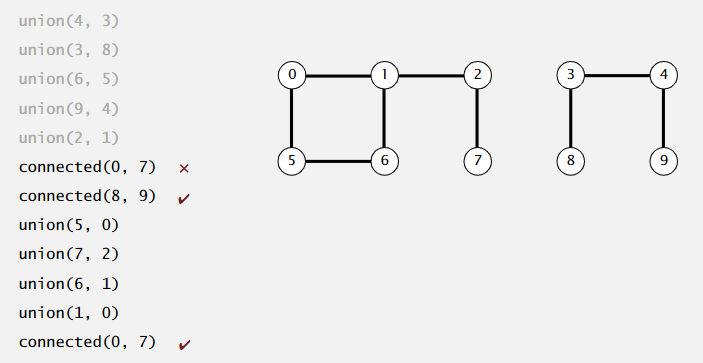
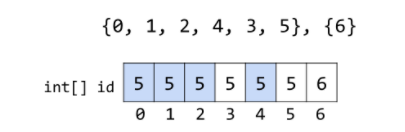
2. 连通举例
假如我们要表示{0, 1, 2, 4}, {3, 5}, {6},在quick find中会表现为:

此时,如果我们想连通2和3,id[2]=4, id[3]=5, quickfind方法会将所有value为4和5的元素统一为相同的value。
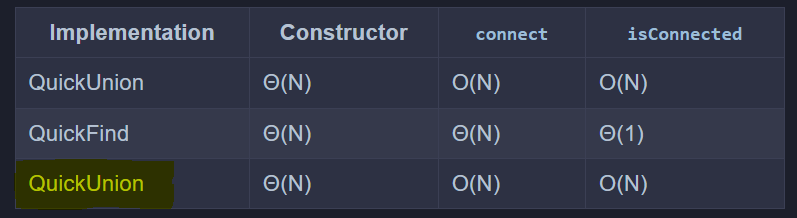
3. 复杂度
It takes N² array accesses to process a sequence of N union commands on N objects.
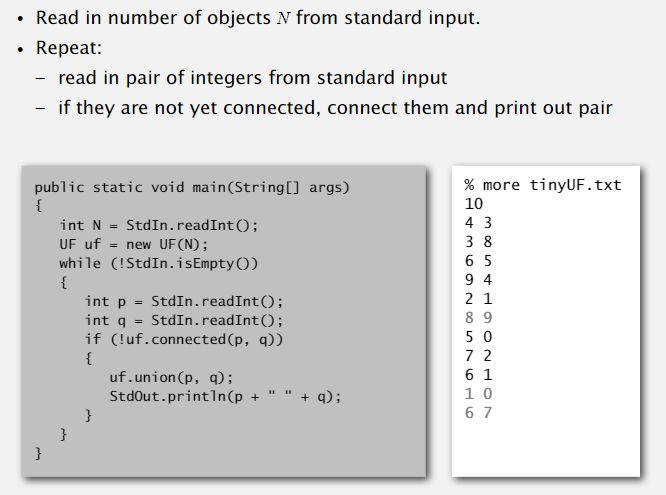
4. Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class QuickFindDS implements DisjointSets {
private int[] id;
/* Θ(N) */
public QuickFindDS(int N){
id = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){
id[i] = i;
}
}
/* need to iterate through the array => Θ(N) */
public void connect(int p, int q){
int pid = id[p];
int qid = id[q];
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++){
if (id[i] == pid){
id[i] = qid;
}
}
}
/* Θ(1) */
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q){
return (id[p] == id[q]);
}
}
III. Quick Union
1. 原理
QuickFind每次连接的时候,需要改变多个value。有没有一个新的方法能使每次连接只改变一个value?
Idea:使用树形结构,每个index的value表示的是它连接的parant。若value为-1,则表示该index为最顶层。
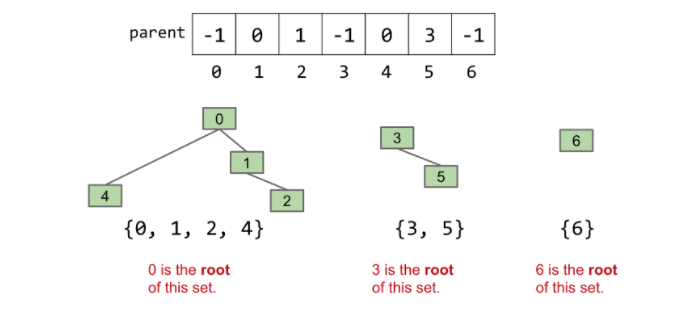
2. 连通举例
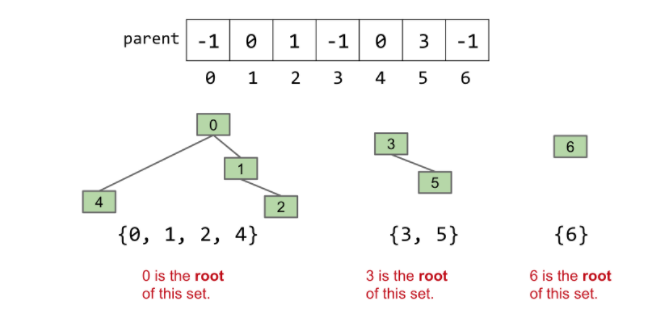
此时,如果我们要连接index 5和index 2:connect(5, 2)
- 找到index 5的root: find(5) -> 3
- 找到index 2的root:find(2) -> 0
- 将index 5的root的值设置为index 2的root的值 -> parent[3]=0
这样就将两个需要连接的元素的root连接了起来,root下所有的元素也都连通了。
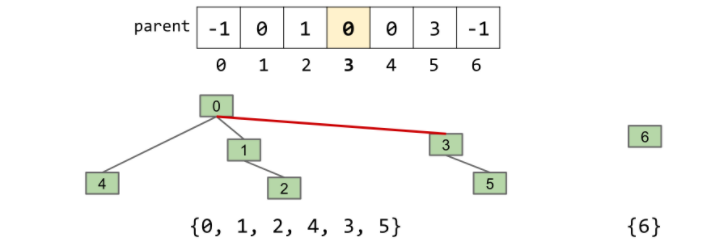
3. 复杂度
4. Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public class QuickUnionDS implements DisjointSets {
private int[] parent;
public QuickUnionDS(int num) {
parent = new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
private int find(int p) {
while (parent[p] >= 0) {
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
@Override
public void connect(int p, int q) {
int i = find(p);
int j= find(q);
parent[i] = j;
}
@Override
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
}
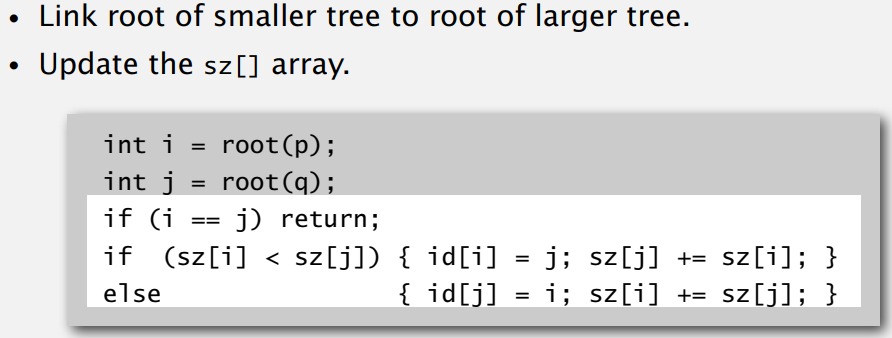
IV. Weighted Quick Union (WQU)
1. 原理
WQU对Quick Union进行优化,不再简单地将第一个元素的root连接到第二个元素的root,而是将size更小的root连接到size较大的root。这样连接后的总体高度相对最小,find root的时间也就更短。
2. 连通举例
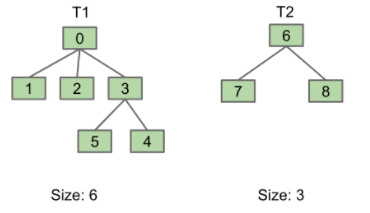
假设我们要连接T1和T2
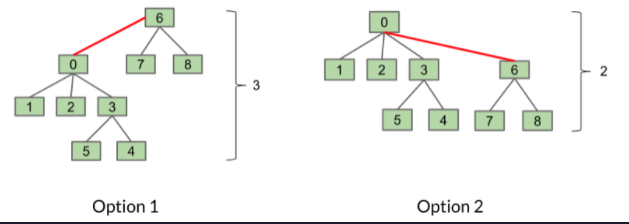
我们会选择Option 2,而不是Option 1.
3. 复杂度
在最坏的情况下,
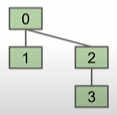
- 当N=1,tree的高度为0

- 当N=2,tree的高度为1
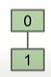
- 当N=4,tree的高度为2
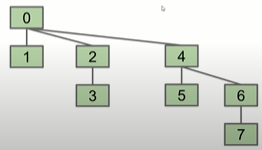
- 当N=8,tree的高度为3
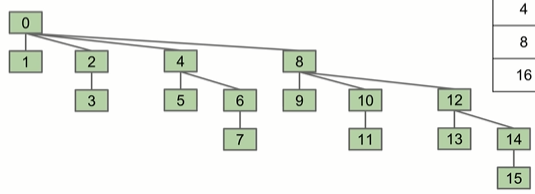
- 当N=16, tree的高度为4
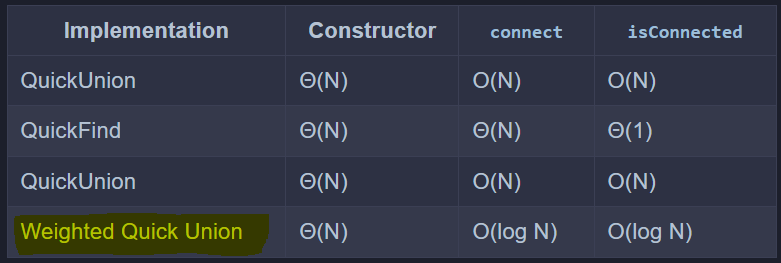
由此可见,最差的情况下的runtime为 Θ(logN).
4. Code
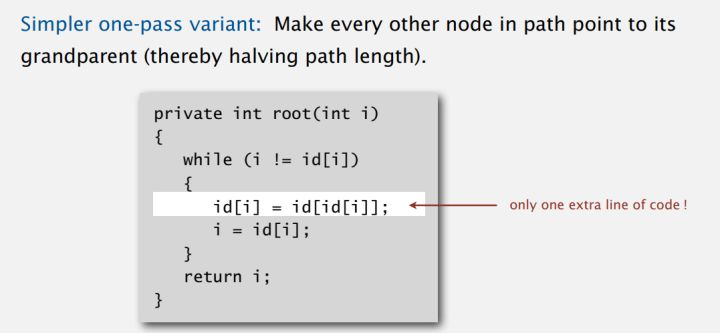
V. Weighted quick-union with path compression
1. 原理
Path compression 是对weighted quick union的优化,它要求每次call connect/isConnect method 时,将该元素所在的路径上所有的元素直接接到root上,这样可以很大程度缩短寻找root的时间。
2. 连通举例
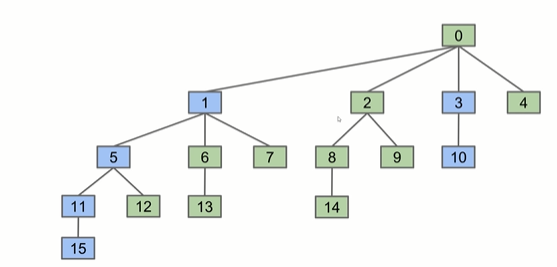
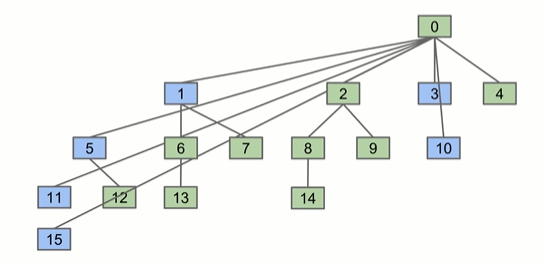
假如我们要判断isConnect(15, 10),我们会分别将15分支和10分支上的所有元素指向对应的root。
3. 复杂度
Iterated logarithm - Wikipedia

4. Code